How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that blends technical understanding with responsible practice. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding the components and pre-flight checks to mastering flight controls and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover essential safety procedures, legal considerations, and troubleshooting common issues, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will provide a structured learning path. We’ll explore various drone models, flight techniques, and image capture strategies, ensuring you gain a holistic understanding of this exciting technology. From basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques, we aim to empower you with the skills and confidence to operate your drone responsibly and creatively.
Drone Components and Their Functions
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight and functionality. This section details the key components and their respective functions.
Drone Propellers and Their Functions
Propellers are the rotating blades that generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, hover, and move. Different propeller designs impact flight performance. Larger propellers generally produce more thrust but may reduce flight time due to increased power consumption. Smaller propellers offer better maneuverability and potentially longer flight times, but at the cost of reduced lift capacity.
- Standard Propellers: These are the most common type, offering a balance of thrust, efficiency, and noise levels.
- Low-Noise Propellers: Designed to minimize noise pollution, often sacrificing some thrust or efficiency.
- High-Thrust Propellers: Optimized for maximum lift, ideal for heavier payloads or challenging conditions, but may reduce flight time.
Drone Motors and Their Functions
Motors are responsible for spinning the propellers. Brushless motors are the standard in most modern drones due to their efficiency, durability, and quieter operation compared to brushed motors.
Flight Controller and Its Function
The flight controller is the drone’s “brain,” responsible for processing data from various sensors and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute flight commands. It uses gyroscopes, accelerometers, and other sensors to track the drone’s orientation and position.
Drone Battery and Its Function
The battery powers all the drone’s components. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are commonly used due to their high energy density. Proper battery care, including safe charging and storage, is essential for optimal performance and safety.
GPS and Its Function
GPS (Global Positioning System) enables the drone to determine its location and maintain its position. This is crucial for features like autonomous flight, Return-to-Home (RTH), and geofencing.
Drone Camera and Its Function
The camera is responsible for capturing aerial photos and videos. Different cameras offer varying resolutions, field of view, and other features to suit different needs.
Comparison of Three Drone Models
The following table compares the features and specifications of three different drone models, illustrating the variety available in the market. Note that specifications can vary based on manufacturer and model revisions.
| Feature | Drone Model A | Drone Model B | Drone Model C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camera Resolution | 4K | 1080p | 4K |
| Flight Time | 25 minutes | 20 minutes | 30 minutes |
| Maximum Range | 5 km | 3 km | 7 km |
| Weight | 1 kg | 0.8 kg | 1.2 kg |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for ensuring safe and responsible drone operation. This minimizes risks and protects both the drone and its surroundings.
Pre-Flight Checklist
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is properly connected.
- Verify GPS signal lock.
- Calibrate the compass if necessary.
- Check the controller batteries.
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Choose a safe and legal flight location, avoiding obstacles and restricted airspace.
- Inform bystanders of your drone operation.
Safety Procedures for Bystanders
Maintaining a safe distance from bystanders is paramount. Communicate clearly with those nearby about your intentions and maintain awareness of their presence. Never fly over crowds or people without their explicit consent. Consider using visual markers or a spotter to enhance safety.
Safety Briefing for Novice Pilots
Before initiating flight, ensure that you understand the basic controls and emergency procedures. Familiarize yourself with the drone’s features and limitations. In case of emergency, immediately switch to RTH mode (if available) or attempt a controlled landing in a safe area. Always prioritize safety.
Taking Off and Landing
Proper takeoff and landing techniques are crucial for safe drone operation. These procedures vary slightly depending on the drone model and environmental conditions.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
For a standard takeoff, gently increase the throttle until the drone lifts off vertically. Maintain a steady ascent, avoiding abrupt movements. Landing involves the reverse process; slowly decrease the throttle until the drone gently touches down. In windy conditions, account for wind gusts and adjust your control inputs accordingly. On uneven terrain, select a flat and stable landing area.
Takeoff and Landing Procedures for Different Drone Types
While the basic principles remain similar, some drone types might have specific procedures. For instance, larger drones may require a more gradual takeoff and landing due to their increased weight and inertia. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific drone model.
Emergency Landing Procedures
In case of unexpected issues, such as low battery or GPS signal loss, prioritize a safe emergency landing. Immediately switch to Return-to-Home (RTH) if available. If RTH is unavailable, smoothly decrease the throttle to perform a controlled descent, selecting a clear landing zone.
Controlling Drone Movement
Understanding the control sticks and their functions is essential for maneuvering the drone effectively. This section details the control inputs and techniques for maintaining stable flight.
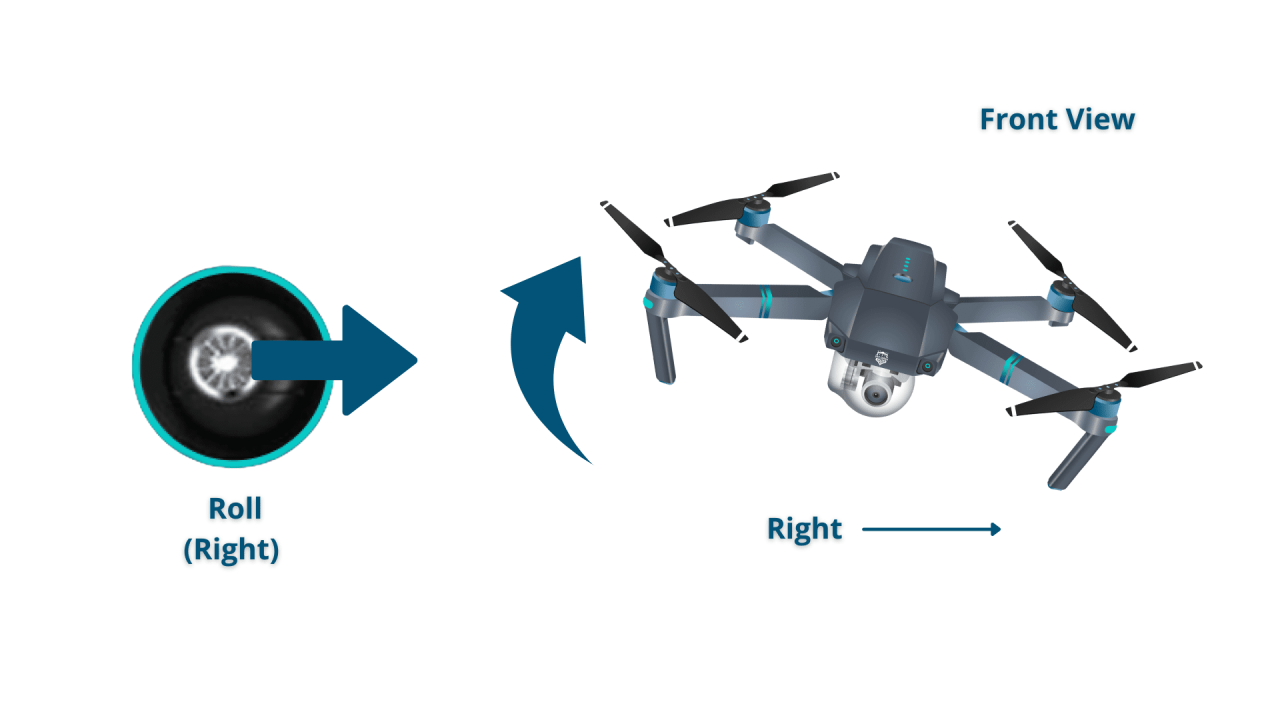
Control Sticks and Their Functions
Most drones use two control sticks: one for controlling altitude and movement along the drone’s forward/backward and side-to-side axes, and the other for controlling the drone’s yaw (rotation) and pitch/roll (tilting). The left stick typically controls altitude and movement, while the right stick controls yaw and tilt.
- Left Stick (Vertical): Up/Down (Throttle), Forward/Backward
- Left Stick (Horizontal): Left/Right (Strafe)
- Right Stick (Vertical): Pitch (Forward/Backward Tilt)
- Right Stick (Horizontal): Yaw (Rotation)
Maintaining Stable Flight
Smooth and controlled movements are key to stable flight. Avoid abrupt inputs, and make small, incremental adjustments to maintain the desired position and altitude. Practice hovering and making minor corrections to build your skills.
Maneuvering Through an Obstacle Course
Navigating an obstacle course requires precise control and planning. Start with simple courses and gradually increase the complexity. Practice making smooth turns, maintaining altitude, and adjusting speed to avoid collisions.
- Plan your route, identifying key turning points and obstacle avoidance strategies.
- Maintain a consistent altitude and speed throughout the course.
- Use small, incremental adjustments to navigate tight turns and obstacles.
- Practice regularly to improve your control and precision.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding your drone’s camera settings and composition techniques. This section explores camera settings and tips for achieving professional-looking results.
Camera Settings and Their Impact
Camera settings like resolution, ISO, shutter speed, and aperture significantly affect image quality. Higher resolution provides more detail, but increases file size. ISO controls sensitivity to light; higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions but may introduce noise. Shutter speed affects motion blur; faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur. Aperture controls depth of field; wider apertures (smaller f-numbers) create shallow depth of field, while narrower apertures (larger f-numbers) create greater depth of field.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
To capture high-quality footage, ensure stable flight, use appropriate camera settings for lighting conditions, and experiment with different angles and perspectives. Use a tripod or other stabilization method for smoother videos. Consider using ND filters to control exposure in bright conditions.
Tips for Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Effective composition is key to compelling aerial imagery. Use the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry to create visually interesting shots. Experiment with different angles and perspectives, and consider the surrounding environment in your composition.
- Use the rule of thirds to position key elements off-center.
- Utilize leading lines to draw the viewer’s eye through the image.
- Incorporate symmetry for visually balanced shots.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives to find unique viewpoints.
Battery Management and Charging
Proper battery care is crucial for extending the lifespan and performance of your drone’s battery. This section details safe charging and storage procedures.
Importance of Proper Battery Care

LiPo batteries have a limited lifespan and require careful handling. Overcharging, discharging too deeply, or improper storage can damage the battery, reducing its capacity and potentially creating safety hazards.
Safe Charging and Storage Procedures, How to operate a drone
Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow the instructions carefully. Never leave batteries unattended while charging. Store LiPo batteries in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials. Before storage, discharge them to around 30-50% of their capacity.
Tips for Extending Flight Time
Optimize flight patterns to minimize power consumption. Avoid aggressive maneuvers that consume excessive power. Keep the drone’s weight as low as possible by removing any unnecessary accessories.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues

Understanding common drone problems and their solutions can save you time and frustration. This section provides troubleshooting tips for common issues.
Common Drone Problems and Their Causes
Common problems include low battery, GPS signal loss, motor failure, and control issues. Low battery is often due to extended flight or overuse. GPS signal loss can result from interference or poor satellite visibility. Motor failure might be due to mechanical issues or overstress. Control issues could stem from faulty connections or controller malfunctions.
Solutions for Troubleshooting Common Issues
For low battery, land immediately and recharge. For GPS signal loss, relocate to an area with better visibility. For motor failure, inspect the motor and replace if necessary. For control issues, check connections and consider recalibrating the controller.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning the basics of controlling the drone’s movements and understanding its various features is crucial, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of safety protocols.
Flowchart for Diagnosing and Resolving Drone Malfunctions
A flowchart can provide a structured approach to troubleshooting. Start by checking the obvious issues, such as battery level and GPS signal. If the problem persists, systematically check other components and connections. Refer to your drone’s manual for detailed troubleshooting guidance.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and understanding of its controls; a great resource to help you learn is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation hinges on consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology and relevant laws.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: How To Operate A Drone
Adhering to local drone regulations and airspace restrictions is crucial for responsible drone operation. This section emphasizes the importance of legal compliance.
Importance of Adhering to Drone Regulations
Flying a drone without adhering to regulations can result in fines, legal repercussions, and potential safety hazards. Regulations vary by location and are designed to ensure safe and responsible airspace management.
Resources for Finding and Understanding Drone Laws
Consult your country’s or region’s aviation authority website for the latest regulations. Many organizations and websites provide information and resources on drone laws and best practices.
Necessary Permits or Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may require permits or licenses to operate a drone. Certain activities, such as commercial drone operation or flying in restricted airspace, often require specific authorization. Check local regulations for details.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers (Optional)
Once you’ve mastered basic drone control, you might explore advanced maneuvers. However, always prioritize safety and practice in a controlled environment.
Performing Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers, such as flips and rolls, require precise control and practice. Start slowly and gradually increase the complexity of your maneuvers. Always maintain awareness of your surroundings and ensure ample space for error.
Risks Associated with Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers increase the risk of accidents due to the higher speed and complexity involved. Loss of control or collisions can result in damage to the drone or injury to bystanders. Practice in a safe, open area away from obstacles and people.
Safely Practicing Advanced Maneuvers
Practice in a safe, open area away from obstacles and people. Start with simple maneuvers and gradually increase the complexity. Always maintain awareness of your surroundings and be prepared to abort a maneuver if necessary. Consult your drone’s manual for guidance on performing advanced maneuvers.
Mastering drone operation involves a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of drone components, safety protocols, flight controls, and image capture techniques. Remember that consistent practice and adherence to safety regulations are crucial for safe and enjoyable drone operation. Embrace the learning process, explore the possibilities, and always prioritize responsible flight practices to ensure a positive and safe experience.
FAQ Guide
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good reviews and ease-of-use features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately initiate a return-to-home (RTH) function if available. If not, carefully guide the drone back using visual cues and land it safely.
How do I clean my drone’s camera lens?
Use a soft microfiber cloth to gently wipe the lens. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.