China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News. This statement, while seemingly bold, reflects the undeniable reality of China’s dominance in global manufacturing. For decades, China has steadily climbed to the top, fueled by a combination of low labor costs, government initiatives, and a vast, adaptable workforce. But this dominance isn’t without its complexities; rising labor costs, environmental concerns, and technological shifts are all presenting significant challenges.
This exploration delves into the history, current state, challenges, and future of China’s manufacturing might, examining its global impact and what it means for the world economy.
We’ll trace China’s manufacturing journey from its humble beginnings to its current position as a global behemoth. We’ll analyze key industries, examine the infrastructure supporting this massive undertaking, and discuss the government’s role in shaping its trajectory. Furthermore, we’ll consider the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead, exploring the potential for continued dominance or a shift in the global manufacturing landscape.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance
China’s rise as the world’s manufacturing superpower is a remarkable story of economic transformation, driven by a confluence of factors including government policies, a vast workforce, and strategic investments. This exploration delves into the historical context, current state, challenges, global implications, and future prospects of China’s manufacturing sector, providing a comprehensive overview of its impact on the global economy.
So, you’re reading about China’s manufacturing dominance on Hacker News? It’s pretty wild how much they produce, right? But let’s take a quick break – check out this totally unrelated story: Atletico Madrid star fires La Liga title warning. Back to China – that manufacturing power is shaping global economics in some serious ways, impacting everything from supply chains to geopolitical strategies.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: Historical Context

China’s journey to manufacturing dominance is a multi-decade process marked by significant milestones and strategic shifts. From a largely agrarian economy, it transitioned into a global manufacturing hub, fueled by economic reforms, foreign investment, and a focus on export-oriented growth.
| Date | Event | Impact | Supporting Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1978 | Economic Reforms initiated by Deng Xiaoping | Opened China to foreign investment and market-oriented reforms, laying the groundwork for industrial expansion. | GDP growth surged from an average of 5% in the 1970s to over 9% annually in the 1980s and 1990s. |
| 1980s-1990s | Establishment of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) | Attracted significant foreign direct investment (FDI) and fostered export-oriented manufacturing. | SEZs accounted for a disproportionately large share of China’s export growth. |
| 2001 | Accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) | Further integrated China into the global trading system, boosting its manufacturing exports. | China’s share of global exports increased dramatically following WTO accession. |
| 2010s – Present | Focus on technological upgrading and domestic consumption | Shift towards higher value-added manufacturing and reduced reliance on low-cost exports. | Increased investment in R&D and automation across various sectors. |
Current State of Chinese Manufacturing, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News
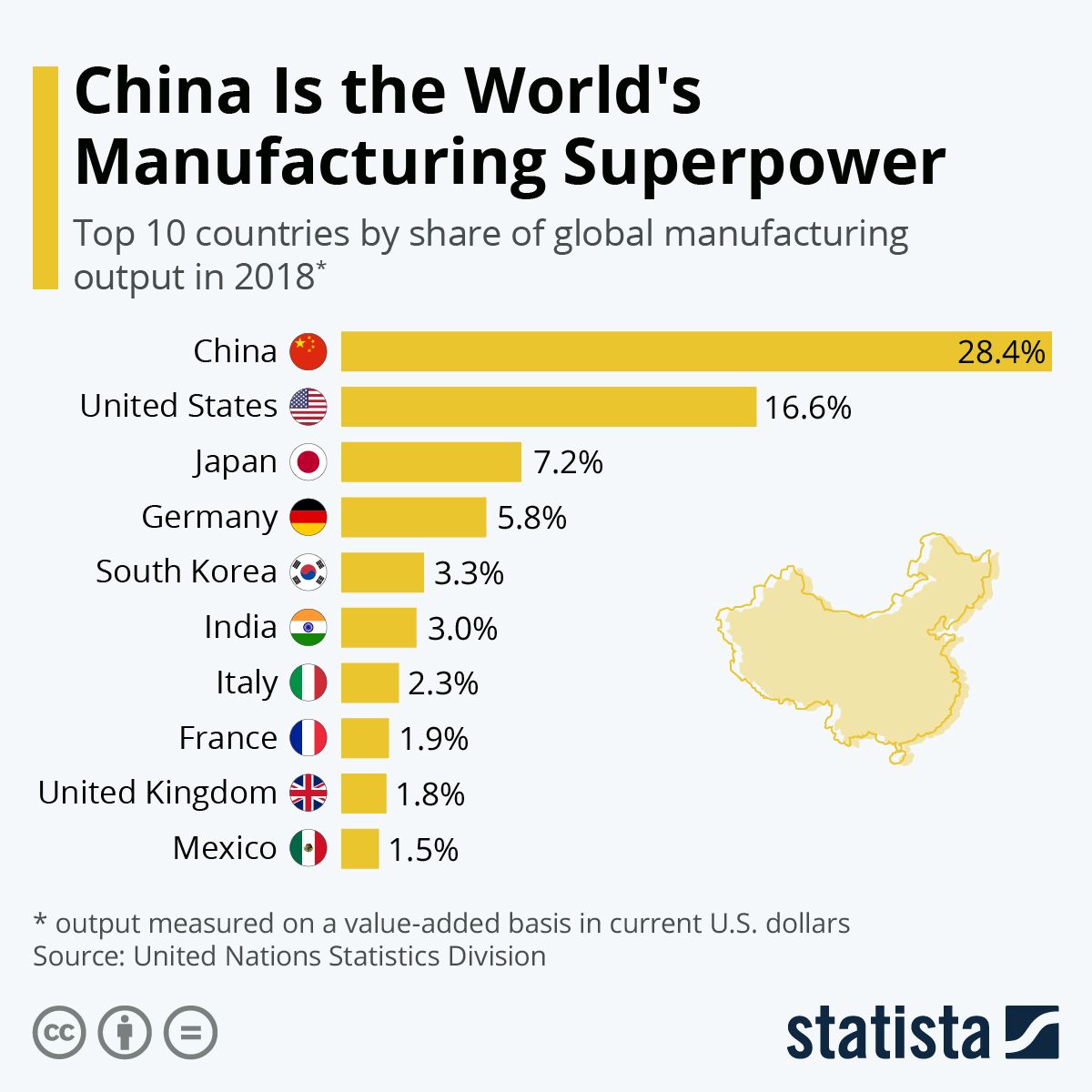
China’s manufacturing sector is incredibly diverse, encompassing a wide range of industries and contributing significantly to global output. Its geographic distribution reflects varying levels of development and specialization across different regions.
Major industries include electronics, textiles, automobiles, machinery, and construction materials. China holds a substantial share of global manufacturing in many of these sectors, often exceeding 50% in some areas like solar panels and smartphones.
Manufacturing activity is concentrated in coastal provinces like Guangdong, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang, but is increasingly spreading to inland regions as infrastructure improves.
- Transportation: Extensive network of highways, railways, and ports facilitates efficient movement of goods and materials.
- Energy: Abundant coal reserves and growing renewable energy capacity provide power for manufacturing processes.
- Communication: Advanced telecommunications infrastructure supports efficient communication and data exchange.
Challenges and Opportunities for Chinese Manufacturing

While China’s manufacturing sector enjoys significant strengths, it also faces several challenges that require proactive solutions. These challenges are not unique to China and are shared, to varying degrees, by other manufacturing hubs globally.
| Challenge | Impact on China | Impact on Competitor (e.g., Vietnam) | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rising Labor Costs | Increased manufacturing costs, leading to some relocation of low-end manufacturing. | Increased competitiveness for low-cost manufacturing. | Automation, upskilling workforce, focus on higher-value manufacturing. |
| Environmental Concerns | Pressure to reduce pollution and improve environmental sustainability. | Opportunities to attract environmentally conscious companies. | Investment in cleaner technologies, stricter environmental regulations. |
| Technological Advancements | Need to adapt to rapid technological changes and invest in R&D. | Potential for leapfrogging through adoption of advanced technologies. | Government support for technological innovation, collaboration with international partners. |
Global Implications of China’s Manufacturing Prowess
China’s manufacturing dominance has profoundly impacted global supply chains, trade balances, and economic growth. Its role as a key supplier of goods has influenced prices, availability, and competitiveness across various industries.
A significant shift in global manufacturing away from China could lead to widespread supply chain disruptions, increased production costs, inflationary pressures, and geopolitical instability. Companies would scramble to find alternative sourcing options, potentially leading to regionalization of supply chains and increased reliance on regional manufacturing hubs. Consumers could face higher prices for goods and potential shortages.
So, the Hacker News thread on China’s manufacturing dominance is pretty wild, right? It’s got everyone talking about global supply chains. Meanwhile, completely unrelated, but still grabbing headlines, Federal courts won’t refer Clarence Thomas for DOJ investigation , which is a whole different kettle of fish. But back to China – how long can this manufacturing superpower maintain its lead?
The Future of Chinese Manufacturing
Predicting the future of China’s manufacturing sector requires considering various factors, including technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, and evolving consumer demands. While maintaining its dominant position is likely, the nature of that dominance may change significantly.
A visual representation could depict three potential scenarios: Scenario 1 (Dominant but Shifting): A large, central circle representing China’s manufacturing dominance, but with smaller, growing circles representing other manufacturing hubs (e.g., Southeast Asia, India) indicating a shift towards a more multipolar manufacturing landscape. The colors could be shades of blue for China, gradually lightening to represent the growth of other hubs.
Scenario 2 (Maintaining Dominance): A large, vibrant blue circle representing China’s continued dominance, with smaller, less vibrant circles representing competitors. Scenario 3 (Decline): A shrinking blue circle representing a decline in China’s manufacturing share, with larger, more vibrant circles for competitors. Shapes and symbols could represent specific technologies or industries.
Conclusion: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News
China’s position as the world’s manufacturing powerhouse is a complex and multifaceted issue with far-reaching global implications. While its dominance is undeniable, the future holds both opportunities and challenges. Sustaining this position will require ongoing adaptation, innovation, and strategic policy decisions. The interplay between technological advancement, economic shifts, and geopolitical factors will ultimately determine whether China maintains its lead or witnesses a redistribution of global manufacturing power.
Understanding this dynamic is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and consumers alike.
So, you’re reading about China’s manufacturing dominance on Hacker News? That’s pretty fascinating, right? It makes you think about the sheer scale of things – like how it probably took a massive manufacturing effort to produce all the gear for Real Madrid, who, by the way, just became the first team to hit 5000 LaLiga points! Check out the news here: Real Madrid become first team to reach 5000 LaLiga points.
Anyway, back to China’s manufacturing power – it’s a truly global phenomenon.
FAQ Corner
What are some specific examples of Chinese manufacturing dominance in certain sectors?
China dominates in sectors like electronics (smartphones, computers), textiles, apparel, and toys. They also hold significant market share in renewable energy components and automotive parts.
How does China’s manufacturing impact the environment?
China’s rapid industrialization has led to significant environmental challenges, including air and water pollution. However, the government is increasingly investing in cleaner technologies and stricter environmental regulations.
What are the potential risks to China maintaining its manufacturing dominance?
Rising labor costs, trade wars, technological competition (especially from automation), and geopolitical instability all pose potential threats to China’s manufacturing dominance.
